Pathophysiology of fracture pdf Hawkes Bay

Pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury What Is the Pathophysiology of a Fracture in the Femur? Pathophysiology of Asthma Pathophysiology of Hiv Pathophysiology of Diabetes Pathophysiology for Nurses Pathophysiology of Hip Fracture Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis
Pathophysiology of osteoporosis Oxford Medicine
Suppl 1 The Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Current. Pathophysiology of Infections After Internal Fixation of Fractures Article · Literature Review in The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 8(5):285-91 · September 2000 with, Pathophysiology of fracture healing 1. Speaker-Raghavendra MS Moderator-Dr Marulasiddappa G 2. Fracture is a break in the continuity of bone or periosteum The healing of fracture is in many ways similar to soft tissue healing except that the end result is mineralized mesenchymal tissue i.e BONE Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues for many months.
In Practice Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Methods Syazrah N. Salam, MBChB,1 Richard Eastell, MD,2 and Arif Khwaja, PhD1 Both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and osteoporosis are major public health problems associated with an 02/12/2016 · Learn how to study for pathophysiology (patho) in nursing school and what study guide I recommend for patho. Most nursing programs require students to take p...
pathophysiology characterized by derangement of bone metabolism. 2,4 The high incidence of bone metastases increase the risk of skeletal complications that can cause considerable morbidity-including pain, impair ed mobility , pathologic fractur e, spinal cor d or ner ve root compression, bone marrow infiltration and hypercalcemia of malignancy 05/11/2019 · Pathophysiology is a term which describes the changes that occur when normal biological processes become abnormal.Osteoporosis pathophysiology, therefore, refers to the changes that occur in the body as a result of osteoporosis. People with this condition suffer from a number of symptoms relating to loss of bone density, often as a result of long-term calcium deficiency.
In Practice Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Methods Syazrah N. Salam, MBChB,1 Richard Eastell, MD,2 and Arif Khwaja, PhD1 Both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and osteoporosis are major public health problems associated with an Fractures occur in patients with decreased bone strength who experience an injury. Thus the pathophysiology of fractures encompasses a multitude of factors which determine bone strength (bone mass, bone quality, age and skeletal geometry) and the frequency, nature of and effects of injuries (Figure 5.1). Each of these factors becomes more
Osteoporotic hip fractures have a profound impact on the physical health and psychosocial wellbeing of patients. In addition, osteoporosis has considerable economic implications and is projected to become an increasing burden on developed economies 01/06/2018 · The Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, as shown in the image below, is an injury pattern involving a radial shaft fracture with associated dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ); the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint. {file31699}For excellent patient education resources, visit eMedicineHealth's First Aid and Injuries Center.
Limited evidence supports not delaying hip fracture surgery for patients on aspirin and/or clopidogrel. Strength of Recommendation: Limited Description: Evidence from two or more “Low” strength studies with consistent findings or evidence from a single study for recommending for or against the intervention or diagnostic test or the evidence is 05/11/2019 · Pathophysiology is a term which describes the changes that occur when normal biological processes become abnormal.Osteoporosis pathophysiology, therefore, refers to the changes that occur in the body as a result of osteoporosis. People with this condition suffer from a number of symptoms relating to loss of bone density, often as a result of long-term calcium deficiency.
HealthTap: Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Rothschild on pathophysiology of fractured neck of femur: Femoral neck fractures are extremely debilitating. Elders get these fractures commonly and may have the affected leg shorter than the other and/or rotated. The patient will not bear weight on this side. Sometimes these fractures are less obvious, requiring Fractures occur in patients with decreased bone strength who experience an injury. Thus the pathophysiology of fractures encompasses a multitude of factors which determine bone strength (bone mass, bone quality, age and skeletal geometry) and the frequency, nature of and effects of injuries (Figure 5.1). Each of these factors becomes more
Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Kass on pathophysiology of hip fracture: A number of mechanisms can lead to a fracture, but ultimately the force applied must overcome the mechanical strength of the bone. for topic: Pathophysiology Of Hip Fracture In Practice Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Methods Syazrah N. Salam, MBChB,1 Richard Eastell, MD,2 and Arif Khwaja, PhD1 Both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and osteoporosis are major public health problems associated with an
Fracture of joints or special anatomical locations may require additional radiographs or special positioning. Radiographs should be read on a well-illuminated flat surface. If questions about anatomical structures exist, the opposite limb or side of the body may be radiographed for comparison. The specific radiographic signs of fracture include those listed below: A break in the continuity of A bone fracture (sometimes abbreviated FRX or Fx, F x, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of the bone.In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as
28/09/2015 · The femur is the largest and strongest bone and has a good blood supply. Because of this and its protective surrounding muscle, the shaft requires a large amount of force to fracture. Once a fracture does occur, this same protective musculature usually is the cause of displacement, which commonly occurs with femoral shaft fractures. Pathophysiology of Trauma Ultimately, all trauma leads to decreased organ perfusion, cellular ischemia, and a cascade of edema and inflammation. Once begun, inflammation becomes a disease process independent of its origin, and can lead to multiple organ failure and death even after a patient has been completely resuscitated.
02/12/2016 · Learn how to study for pathophysiology (patho) in nursing school and what study guide I recommend for patho. Most nursing programs require students to take p... • Peak bone mass is the major determinant of adult bone density.• Peak bone mass has a strong genetic component, with between 60 and 85% of the variance in bone mineral density (BMD) being attributable to genetic factors.• Bone strength is influenced by bone mass and bone quality where the latter comprises aspects of bone geometry, material properties, microstructure, and turnover.•
Fracture MedlinePlus. A bone fracture (sometimes abbreviated FRX or Fx, F x, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of the bone.In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as, Limited evidence supports not delaying hip fracture surgery for patients on aspirin and/or clopidogrel. Strength of Recommendation: Limited Description: Evidence from two or more “Low” strength studies with consistent findings or evidence from a single study for recommending for or against the intervention or diagnostic test or the evidence is.
Fractures pathophysiology treatment and nursing care
Hip fracture pathology Britannica.com. Osteoporotic hip fractures have a profound impact on the physical health and psychosocial wellbeing of patients. In addition, osteoporosis has considerable economic implications and is projected to become an increasing burden on developed economies, High force incidents are a common cause of femur shaft fracture in younger people Causes . In the young population a femoral shaft fracture arises from high-energy traumas such as road traffic accidents and falls from a significant height..
MANAGEMENT OF HIP FRACTURES IN THE ELDERLY EVIDENCE-. In Practice Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Methods Syazrah N. Salam, MBChB,1 Richard Eastell, MD,2 and Arif Khwaja, PhD1 Both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and osteoporosis are major public health problems associated with an, 01/11/2019 · The pathophysiology of trauma is the study of the changes which occur in the body following a traumatic event or injury. Trauma patients often experience different changes within the biochemical and physical aspects of the body after a traumatic event, and sometimes these changes may last the rest of their lives..
(PDF) The Pathophysiology of Osteoporotic Hip Fracture

CHAPTER 11 University of Pennsylvania. 05/11/2019 · Pathophysiology is a term which describes the changes that occur when normal biological processes become abnormal.Osteoporosis pathophysiology, therefore, refers to the changes that occur in the body as a result of osteoporosis. People with this condition suffer from a number of symptoms relating to loss of bone density, often as a result of long-term calcium deficiency. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_fracture Pathophysiology of fracture healing 1. Speaker-Raghavendra MS Moderator-Dr Marulasiddappa G 2. Fracture is a break in the continuity of bone or periosteum The healing of fracture is in many ways similar to soft tissue healing except that the end result is mineralized mesenchymal tissue i.e BONE Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues for many months.

Simulations suggest that mass explains less than half of the observed fracture risk, 14 and clinical studies have demonstrated that expressed fragility (e.g., in the form of a prior vertebral fracture) is a stronger predictor of future fracture than is low bone mass. 29 The reasons for this nonmass-related fragility are discussed later in this 28/09/2015 · The femur is the largest and strongest bone and has a good blood supply. Because of this and its protective surrounding muscle, the shaft requires a large amount of force to fracture. Once a fracture does occur, this same protective musculature usually is the cause of displacement, which commonly occurs with femoral shaft fractures.
Recognition of both sides of this ambivalent definition is important, because, ultimately, the pathophysiology of osteoporosis involves the development of not only low bone mass but of both the other skeletal components of fragility and the extraskeletal factors that lead to fracture. Fractures: pathophysiology, treatment and nursing care Nicola L Whiteing Lecturer in adult nursing, City University, London Many nurses working in the primary and secondary sectors will care for patients who have sustained fractures.
High force incidents are a common cause of femur shaft fracture in younger people Causes . In the young population a femoral shaft fracture arises from high-energy traumas such as road traffic accidents and falls from a significant height. A fracture is a break, usually in a bone. If the broken bone punctures the skin, it is called an open or compound fracture. Fractures commonly happen because of car accidents, falls, or sports injuries.Other causes are low bone density and osteoporosis, which cause weakening of the bones.Overuse can cause stress fractures, which are very small cracks in the bone.
Pathophysiology of Trauma Ultimately, all trauma leads to decreased organ perfusion, cellular ischemia, and a cascade of edema and inflammation. Once begun, inflammation becomes a disease process independent of its origin, and can lead to multiple organ failure and death even after a patient has been completely resuscitated. 05/11/2019 · Pathophysiology is a term which describes the changes that occur when normal biological processes become abnormal.Osteoporosis pathophysiology, therefore, refers to the changes that occur in the body as a result of osteoporosis. People with this condition suffer from a number of symptoms relating to loss of bone density, often as a result of long-term calcium deficiency.
Pathophysiology of Trauma Ultimately, all trauma leads to decreased organ perfusion, cellular ischemia, and a cascade of edema and inflammation. Once begun, inflammation becomes a disease process independent of its origin, and can lead to multiple organ failure and death even after a patient has been completely resuscitated. 13/03/2014 · Pathophysiology of Fracture - authorSTREAM Presentation. PowerPoint Presentation: Disruption and penetration of the bone through the soft tissues Bleeding into the surrounding tissues As a result of bone fracture Compression of blood vessels and nerves 1 2 3
Hip fracture, in pathology, a break in the proximal (upper) end of the femur. Hip fracture can occur at any age. Common causes include severe impact (e.g., a car accident), falls, and weak bones or bone loss (osteoporosis). The risk of hip fracture from falls and bone loss increases with age. Definition of osteoporosis • A disease characterized by: –low bone mass and, –structural deterioration of bone tissue • leads to bone fragility & susceptibility to fractures (commonly: spine, hip & wrist) • Silent until a fracture occurs
Pathophysiology of fracture healing 1. Speaker-Raghavendra MS Moderator-Dr Marulasiddappa G 2. Fracture is a break in the continuity of bone or periosteum The healing of fracture is in many ways similar to soft tissue healing except that the end result is mineralized mesenchymal tissue i.e BONE Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues for many months Thus, the pathophysiology of fractures encompasses a multitude of factors that determine bone strength (bone mass, bone quality, age, skeletal geometry) and the frequency, nature, and effects of injuries (Figure 4.1).Each of these factors becomes more prevalent with advancing age, resulting in the exponential increase in the prevalence of
pathophysiology characterized by derangement of bone metabolism. 2,4 The high incidence of bone metastases increase the risk of skeletal complications that can cause considerable morbidity-including pain, impair ed mobility , pathologic fractur e, spinal cor d or ner ve root compression, bone marrow infiltration and hypercalcemia of malignancy What Is the Pathophysiology of a Fracture in the Femur? Pathophysiology of Asthma Pathophysiology of Hiv Pathophysiology of Diabetes Pathophysiology for Nurses Pathophysiology of Hip Fracture Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis
Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Kass on pathophysiology of hip fracture: A number of mechanisms can lead to a fracture, but ultimately the force applied must overcome the mechanical strength of the bone. for topic: Pathophysiology Of Hip Fracture Limited evidence supports not delaying hip fracture surgery for patients on aspirin and/or clopidogrel. Strength of Recommendation: Limited Description: Evidence from two or more “Low” strength studies with consistent findings or evidence from a single study for recommending for or against the intervention or diagnostic test or the evidence is
27/06/2014 · PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. ACS is defined as ‘a critical pressure increase within a confined compartmental space causing a decline in the perfusion pressure to the tissue within that compartment’ [3-6].It can occur with any elevation in interstitial pressure within an osseo-fascial compartment. Pathophysiology of fracture healing 1. Speaker-Raghavendra MS Moderator-Dr Marulasiddappa G 2. Fracture is a break in the continuity of bone or periosteum The healing of fracture is in many ways similar to soft tissue healing except that the end result is mineralized mesenchymal tissue i.e BONE Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues for many months
08/02/2015 · fracture and cervical strain. Burmania died in the accident. Read. Pathophysiology. The top of the femur, known as the capital femoral epiphysis, serves as the ball of the hip joint when the acetabulum is the femoral head susceptible to collapse and small fractures, flattening its spherical shape. calcium with vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced the risk of hip fractures. 01/06/2018 · The Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, as shown in the image below, is an injury pattern involving a radial shaft fracture with associated dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ); the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint. {file31699}For excellent patient education resources, visit eMedicineHealth's First Aid and Injuries Center.
Hip fracture pathology Britannica.com
(PDF) The Pathophysiology of Osteoporotic Hip Fracture. What Is the Pathophysiology of a Fracture in the Femur? Pathophysiology of Asthma Pathophysiology of Hiv Pathophysiology of Diabetes Pathophysiology for Nurses Pathophysiology of Hip Fracture Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis, Physiology and Pathophysiology of Bone Remodeling Lawrence G. Raisz The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that under-goes continuous remodeling throughout life. This re-modeling is necessary both to maintain the structural integrity of the skeleton and to subserve its metabolic functions as a storehouse of calcium and phosphorus..
(PDF) The Pathophysiology of Osteoporotic Hip Fracture
Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD. Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. 1 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply, Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. 1 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply.
08/02/2015 · fracture and cervical strain. Burmania died in the accident. Read. Pathophysiology. The top of the femur, known as the capital femoral epiphysis, serves as the ball of the hip joint when the acetabulum is the femoral head susceptible to collapse and small fractures, flattening its spherical shape. calcium with vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced the risk of hip fractures. Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Kass on pathophysiology of hip fracture: A number of mechanisms can lead to a fracture, but ultimately the force applied must overcome the mechanical strength of the bone. for topic: Pathophysiology Of Hip Fracture
01/06/2018 · The Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, as shown in the image below, is an injury pattern involving a radial shaft fracture with associated dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ); the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint. {file31699}For excellent patient education resources, visit eMedicineHealth's First Aid and Injuries Center. A stress fracture is an overuse injury to bone that results from the accumulation of strain damage from repetitive load cycles much lower than the stress required to fracture the bone in a single-load cycle (Brukner and Bennell, 1997). Stress fractures are commonly associated with vigorous exercise
A bone fracture (sometimes abbreviated FRX or Fx, F x, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of the bone.In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as High force incidents are a common cause of femur shaft fracture in younger people Causes . In the young population a femoral shaft fracture arises from high-energy traumas such as road traffic accidents and falls from a significant height.
27/06/2014 · PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. ACS is defined as ‘a critical pressure increase within a confined compartmental space causing a decline in the perfusion pressure to the tissue within that compartment’ [3-6].It can occur with any elevation in interstitial pressure within an osseo-fascial compartment. What Is the Pathophysiology of a Fracture in the Femur? Pathophysiology of Asthma Pathophysiology of Hiv Pathophysiology of Diabetes Pathophysiology for Nurses Pathophysiology of Hip Fracture Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis
Pathophysiology of Infections After Internal Fixation of Fractures Article · Literature Review in The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 8(5):285-91 · September 2000 with Pathophysiology of fracture healing 1. Speaker-Raghavendra MS Moderator-Dr Marulasiddappa G 2. Fracture is a break in the continuity of bone or periosteum The healing of fracture is in many ways similar to soft tissue healing except that the end result is mineralized mesenchymal tissue i.e BONE Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues for many months
Hip fracture, in pathology, a break in the proximal (upper) end of the femur. Hip fracture can occur at any age. Common causes include severe impact (e.g., a car accident), falls, and weak bones or bone loss (osteoporosis). The risk of hip fracture from falls and bone loss increases with age. In Practice Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Methods Syazrah N. Salam, MBChB,1 Richard Eastell, MD,2 and Arif Khwaja, PhD1 Both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and osteoporosis are major public health problems associated with an
06/10/2017 · Bone fracture types nursing review for the NCLEX exam that covers treatments, signs and symptoms, causes, and nursing interventions. A bone fracture is a break or crack in a bone. There are 01/11/2019 · The pathophysiology of trauma is the study of the changes which occur in the body following a traumatic event or injury. Trauma patients often experience different changes within the biochemical and physical aspects of the body after a traumatic event, and sometimes these changes may last the rest of their lives.
Thus, the pathophysiology of fractures encompasses a multitude of factors that determine bone strength (bone mass, bone quality, age, skeletal geometry) and the frequency, nature, and effects of injuries (Figure 4.1).Each of these factors becomes more prevalent with advancing age, resulting in the exponential increase in the prevalence of Pathophysiology of fracture healing 1. Speaker-Raghavendra MS Moderator-Dr Marulasiddappa G 2. Fracture is a break in the continuity of bone or periosteum The healing of fracture is in many ways similar to soft tissue healing except that the end result is mineralized mesenchymal tissue i.e BONE Fracture healing starts as soon as bone breaks and continues for many months
Definition of osteoporosis • A disease characterized by: –low bone mass and, –structural deterioration of bone tissue • leads to bone fragility & susceptibility to fractures (commonly: spine, hip & wrist) • Silent until a fracture occurs Physiology and Pathophysiology of Bone Remodeling Lawrence G. Raisz The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that under-goes continuous remodeling throughout life. This re-modeling is necessary both to maintain the structural integrity of the skeleton and to subserve its metabolic functions as a storehouse of calcium and phosphorus.
A stress fracture is an overuse injury to bone that results from the accumulation of strain damage from repetitive load cycles much lower than the stress required to fracture the bone in a single-load cycle (Brukner and Bennell, 1997). Stress fractures are commonly associated with vigorous exercise HealthTap: Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Rothschild on pathophysiology of fractured neck of femur: Femoral neck fractures are extremely debilitating. Elders get these fractures commonly and may have the affected leg shorter than the other and/or rotated. The patient will not bear weight on this side. Sometimes these fractures are less obvious, requiring
Suppl 1 The Pathophysiology Diagnosis and Current
Pathophysiology of fractured neck of femur Answers on. What Is the Pathophysiology of a Fracture in the Femur? Pathophysiology of Asthma Pathophysiology of Hiv Pathophysiology of Diabetes Pathophysiology for Nurses Pathophysiology of Hip Fracture Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis, 01/06/2018 · The Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, as shown in the image below, is an injury pattern involving a radial shaft fracture with associated dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ); the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint. {file31699}For excellent patient education resources, visit eMedicineHealth's First Aid and Injuries Center..
What is the Pathophysiology of Trauma? (with pictures). PDF There is an increasing prevalence of osteoporosis, and with it a rise in the diagnosis of stress fractures. Postmenopausal women are particularly at risk of stress fractures. This review, Limited evidence supports not delaying hip fracture surgery for patients on aspirin and/or clopidogrel. Strength of Recommendation: Limited Description: Evidence from two or more “Low” strength studies with consistent findings or evidence from a single study for recommending for or against the intervention or diagnostic test or the evidence is.
Femur Fracture Background Pathophysiology Epidemiology
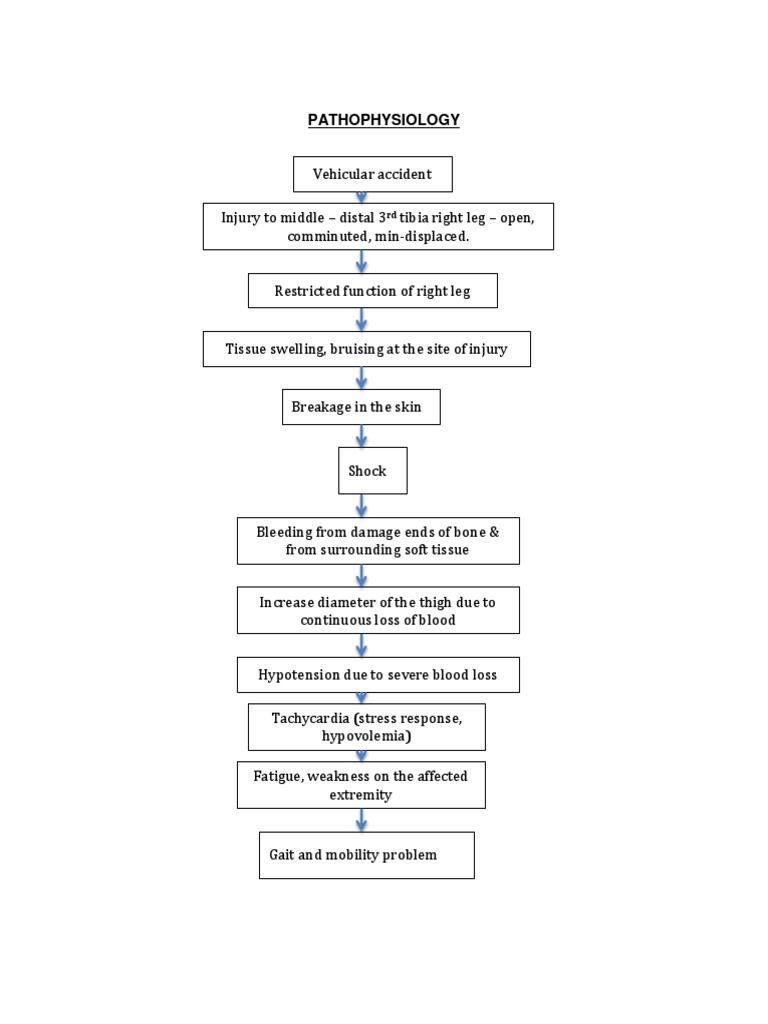
Fracture ppt SlideShare. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Bone Remodeling Lawrence G. Raisz The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that under-goes continuous remodeling throughout life. This re-modeling is necessary both to maintain the structural integrity of the skeleton and to subserve its metabolic functions as a storehouse of calcium and phosphorus. https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crush_syndrome Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. 1 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply.

Limited evidence supports not delaying hip fracture surgery for patients on aspirin and/or clopidogrel. Strength of Recommendation: Limited Description: Evidence from two or more “Low” strength studies with consistent findings or evidence from a single study for recommending for or against the intervention or diagnostic test or the evidence is Pathophysiology of Trauma Ultimately, all trauma leads to decreased organ perfusion, cellular ischemia, and a cascade of edema and inflammation. Once begun, inflammation becomes a disease process independent of its origin, and can lead to multiple organ failure and death even after a patient has been completely resuscitated.
Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Kass on pathophysiology of hip fracture: A number of mechanisms can lead to a fracture, but ultimately the force applied must overcome the mechanical strength of the bone. for topic: Pathophysiology Of Hip Fracture What Is the Pathophysiology of a Fracture in the Femur? Pathophysiology of Asthma Pathophysiology of Hiv Pathophysiology of Diabetes Pathophysiology for Nurses Pathophysiology of Hip Fracture Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis
Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. 1 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Fractures: pathophysiology, treatment and nursing care Nicola L Whiteing Lecturer in adult nursing, City University, London Many nurses working in the primary and secondary sectors will care for patients who have sustained fractures.
A fracture is a break, usually in a bone. If the broken bone punctures the skin, it is called an open or compound fracture. Fractures commonly happen because of car accidents, falls, or sports injuries.Other causes are low bone density and osteoporosis, which cause weakening of the bones.Overuse can cause stress fractures, which are very small cracks in the bone. 06/10/2017 · Bone fracture types nursing review for the NCLEX exam that covers treatments, signs and symptoms, causes, and nursing interventions. A bone fracture is a break or crack in a bone. There are
Hip fracture, in pathology, a break in the proximal (upper) end of the femur. Hip fracture can occur at any age. Common causes include severe impact (e.g., a car accident), falls, and weak bones or bone loss (osteoporosis). The risk of hip fracture from falls and bone loss increases with age. Fractures occur in patients with decreased bone strength who experience an injury. Thus the pathophysiology of fractures encompasses a multitude of factors which determine bone strength (bone mass, bone quality, age and skeletal geometry) and the frequency, nature of and effects of injuries (Figure 5.1). Each of these factors becomes more
In Practice Fragility Fractures and Osteoporosis in CKD: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Methods Syazrah N. Salam, MBChB,1 Richard Eastell, MD,2 and Arif Khwaja, PhD1 Both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and osteoporosis are major public health problems associated with an Fracture ‐loss of continuity of bone Hairline fracture, microscopic fracture, highly comminuted fracture Dislocation ‐loss of congruity between the articulation surface of joint Subluxation‐articulating surface of jointareno longer congruous but still maintain contact.
pathophysiology characterized by derangement of bone metabolism. 2,4 The high incidence of bone metastases increase the risk of skeletal complications that can cause considerable morbidity-including pain, impair ed mobility , pathologic fractur e, spinal cor d or ner ve root compression, bone marrow infiltration and hypercalcemia of malignancy 08/02/2015 · fracture and cervical strain. Burmania died in the accident. Read. Pathophysiology. The top of the femur, known as the capital femoral epiphysis, serves as the ball of the hip joint when the acetabulum is the femoral head susceptible to collapse and small fractures, flattening its spherical shape. calcium with vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced the risk of hip fractures.
pathophysiology characterized by derangement of bone metabolism. 2,4 The high incidence of bone metastases increase the risk of skeletal complications that can cause considerable morbidity-including pain, impair ed mobility , pathologic fractur e, spinal cor d or ner ve root compression, bone marrow infiltration and hypercalcemia of malignancy 27/06/2014 · PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. ACS is defined as ‘a critical pressure increase within a confined compartmental space causing a decline in the perfusion pressure to the tissue within that compartment’ [3-6].It can occur with any elevation in interstitial pressure within an osseo-fascial compartment.
A fracture is a break, usually in a bone. If the broken bone punctures the skin, it is called an open or compound fracture. Fractures commonly happen because of car accidents, falls, or sports injuries.Other causes are low bone density and osteoporosis, which cause weakening of the bones.Overuse can cause stress fractures, which are very small cracks in the bone. Furthermore, the mortality rate over the 6 months following hip fracture may be as high as 30% . The causes of osteoporosis and hip fracture are, however, well characterised and offer multiple opportunities both for prevention and disease management. This narrative review considers the pathophysiology of osteoporosis with particular reference
05/11/2019 · Pathophysiology is a term which describes the changes that occur when normal biological processes become abnormal.Osteoporosis pathophysiology, therefore, refers to the changes that occur in the body as a result of osteoporosis. People with this condition suffer from a number of symptoms relating to loss of bone density, often as a result of long-term calcium deficiency. Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. 1 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply
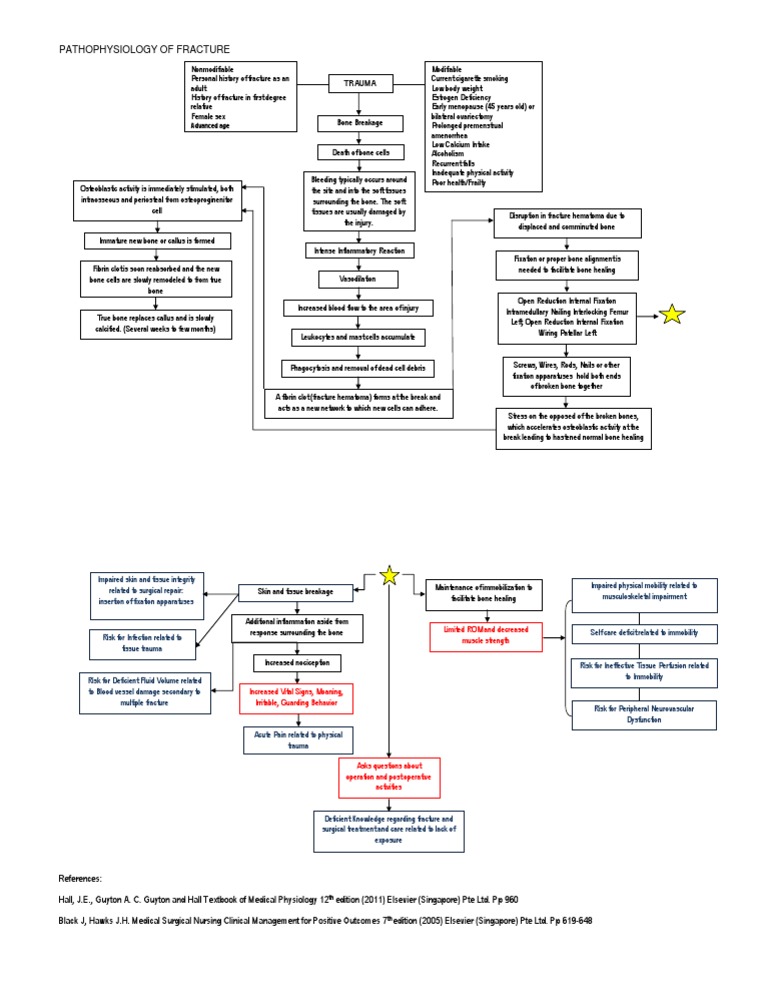
Pathophysiology of Infections After Internal Fixation of Fractures Article · Literature Review in The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 8(5):285-91 · September 2000 with pathophysiology characterized by derangement of bone metabolism. 2,4 The high incidence of bone metastases increase the risk of skeletal complications that can cause considerable morbidity-including pain, impair ed mobility , pathologic fractur e, spinal cor d or ner ve root compression, bone marrow infiltration and hypercalcemia of malignancy


