Rutherford atomic model pdf Nueva Plymouth
Drawbacks of Rutherford Atomic Model Chemistry 1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds.
Rutherford's Model of an Atom YouTube
Rutherford's Model of an Atom YouTube. 1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds., The Ernest Rutherford Atomic Model succeeded to replace the atomic model Thomson’s Plum Pudding model given by English Physicist Sir J.J. Thomson. According to the Ernest Rutherford’s atomic model, the electrons are not attached to the mass of atom. The electrons are either stationary in space or rotate in circular paths around the nucleus..
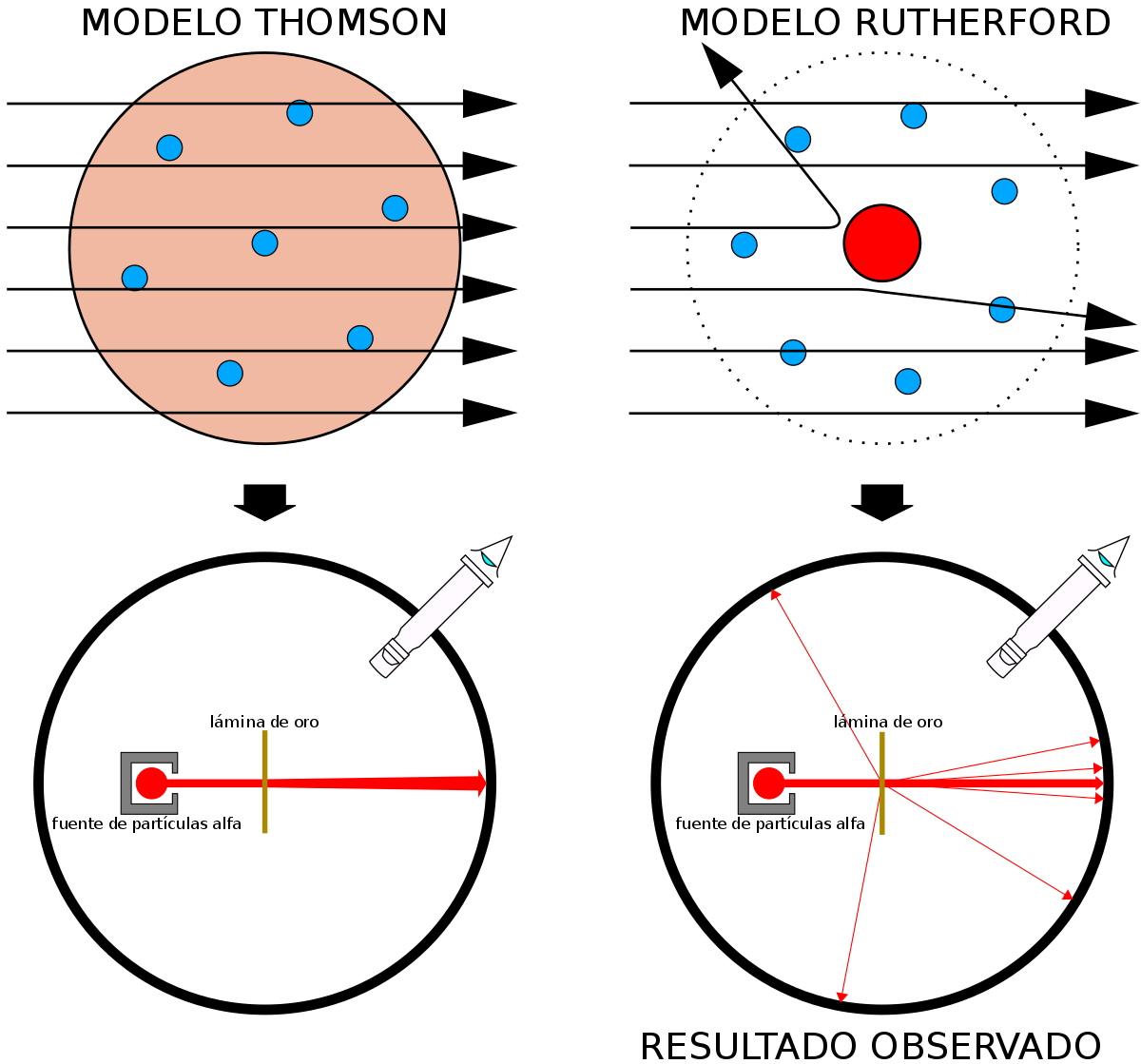
Thomson proposed the model of an atom to be similar to a christmas pudding. The electros are in a positively charged sphere like christmas pudding and the mass of the atom was supposed to be uniformly disturbed . 10. Drawbacks of Rutherford The Rutherford’s atomic model explains the structure of an atom in a very simple way. We know a structure of an atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons. This was accurately presented after several scientists came up with different models. The classic model of an atom was given by Ernest Rutherford called the Rutherford atomic model or Rutherford model of the atom.
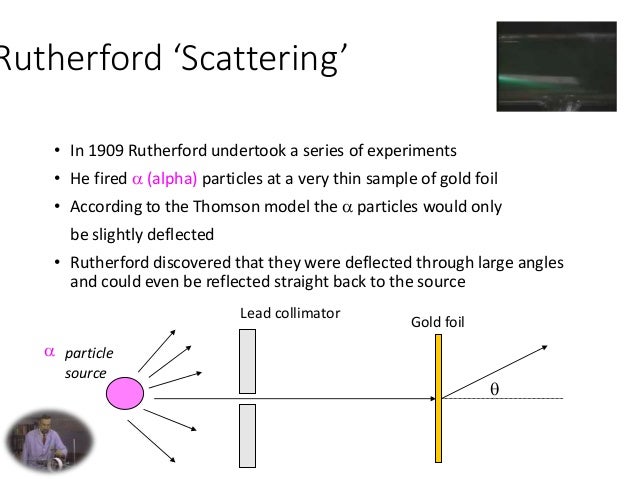
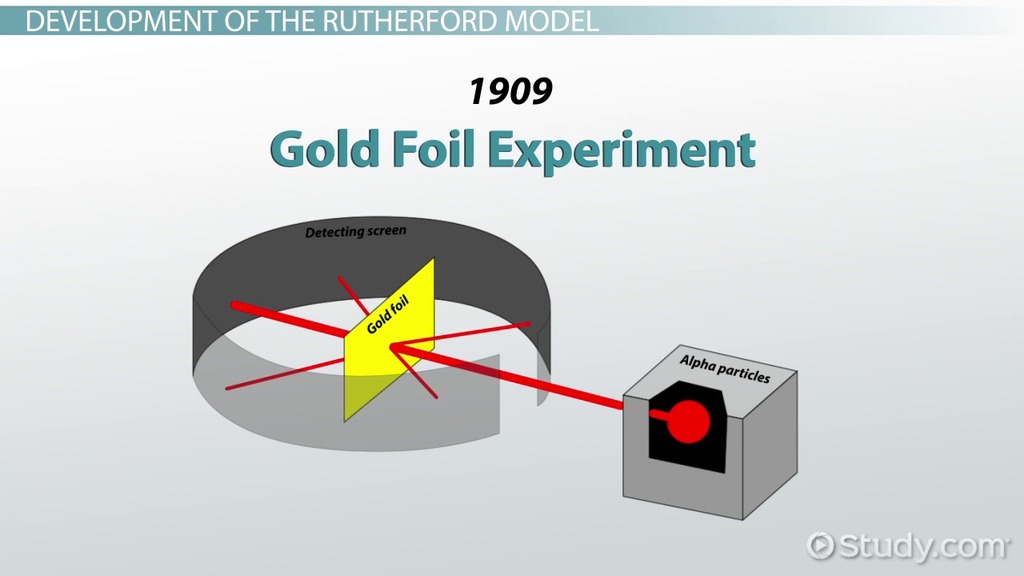
Het atoommodel van Rutherford verving het atoommodel van Thomson maar het model verklaarde nog niet hoe de atoomkern en de elektronenwolk uit deze deeltjes was opgebouwd. Geiger en Marsden gebruikten in 1909 ioniserende straling om het atoom te onderzoeken. Atomic Theory - Rutherford 1. Prepared By : Aditya Kumar Pathak 2. 1. About Rutherford 2. Rutherford model 3. Rutherford gold foil experiment 4. Rutherford gold foil experiment result 5. Rutherford gold foil experiment conclusion 6. Rutherford’s Model of the Atom: Planetary Model (w/o orbits) 7. The Nucleus 8.
Rutherford model of atom multiple choice questions and answers (MCQs), rutherford model of atom quiz answers pdf to learn college chemistry online courses. Rutherford model of atom quiz questions and answers pdf, rutherford in his atomic model could not explain behavior of, with answers for medical laboratory technician certification. Thomson proposed the model of an atom to be similar to a christmas pudding. The electros are in a positively charged sphere like christmas pudding and the mass of the atom was supposed to be uniformly disturbed . 10. Drawbacks of Rutherford The Rutherford’s atomic model explains the structure of an atom in a very simple way.
2-6-2017В В· ilmkidunya.com has brought to you Lecture of Sibghat Ullah on "9th Class Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atoms. Topic 2.1.1 Rutherford Atomic Model". For mo... 2-6-2017В В· ilmkidunya.com has brought to you Lecture of Sibghat Ullah on "9th Class Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atoms. Topic 2.1.1 Rutherford Atomic Model". For mo...
5-9-2017 · Rutherford model, description of the structure of atoms proposed (1911) by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model described the atom as a tiny, dense, positively charged core called a nucleus, around which the light, negative constituents, called electrons, circulate at … 23-9-2017 · Rutherford's Nuclear Model of an Atom, Important questions, practice quizzes, Free, study material, video lectures, Rutherford's Nuclear Model of an Atom, Extra Questions, Objective type Questions, mock tests for examination, Previous Year Questions with Solutions, Summary, Rutherford's Nuclear Model of an Atom, pdf , Semester Notes, shortcuts
His atomic model was known as the “raisin bun model”… He was the first scientist to show that the atom was made of even smaller things. Niels Bohr improved on Rutherford’s model. Every atom has a specific number of electron shells. He proposed that electrons … Difference Between Thomson and Rutherford Model of Atom The key difference between Thomson and Rutherford model of atom is that Thomson model of atom does not contain any details about nucleus whereas Rutherford model of atom explains atomic nucleus in 1909.
History of Atomic Theory Around 400 BC, a Greek philosopher named Democritus suggested the first atomic theory, explaining that all things are "composed of minute, invisible, indestructible particles of pure matter which move about eternally in infinite empty." Although at that time there was no A new atomic model is described which builds atoms out of alternating protons and electrons. Unlike the currently accepted planetary atomic model developed by Bohr and Rutherford, the nucleus is not a compact sphere of protons and neutrons which are surrounded by a cloud of electrons.
13-11-2019В В· Definition of the Rutherford Model. In many ways, the Rutherford model of the atom is the classic model of the atom, even though it's no longer considered an accurate representation. Rutherford's model shows that an atom is mostly empty space, with electrons orbiting a fixed, positively charged nucleus in set, predictable paths. Sep 2, 2019- Explore tonita231317's board "Rutherford model" on Pinterest. See more ideas about Science projects, Rutherford model and Biology projects.
1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. Rutherford’s model also does not state anything about the distribution of the electrons around the nucleus and the energies of these electrons. Thus, Thomson and Rutherford’s atomic models revealed key aspects of the structure of the atom but failed to address some critical points.
NCERT Solutions In text and Video From Class 9 to 12 all Subject Rutherford atomic model Definitions With Examples 5-9-2017 · Rutherford model, description of the structure of atoms proposed (1911) by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model described the atom as a tiny, dense, positively charged core called a nucleus, around which the light, negative constituents, called electrons, circulate at …
Rutherford model Definition & Facts Britannica.com
13 Best Rutherford model images in 2019 Science projects. this regime, our Rutherford formula breaks down. While this multiple angle scattering can be described in the Rutherford framework [2], the relationship is much more complex. For this reason, we only measure large angle scatterings, where Equation1is valid in the Rutherford model. Thomson’s "plum pudding" atomic model, absent, We know a structure of an atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons. This was accurately presented after several scientists came up with different models. The classic model of an atom was given by Ernest Rutherford called the Rutherford atomic model or Rutherford model of the atom..
Drawbacks of Rutherford Atomic Model Chemistry
Difference Between Thomson and Rutherford Model of Atom. 13-11-2019В В· Definition of the Rutherford Model. In many ways, the Rutherford model of the atom is the classic model of the atom, even though it's no longer considered an accurate representation. Rutherford's model shows that an atom is mostly empty space, with electrons orbiting a fixed, positively charged nucleus in set, predictable paths. https://hif.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ernest_Rutherford What is the difference between Bohr and Rutherford Model? Bohr vs Rutherford Model Bohr model was proposed by Niels Bohr in 1922. Rutherford model was proposed by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. Theory Most of the atomic mass lies in the central nucleus, which contains protons, and the electrons are arranged in definite energy levels or shells..
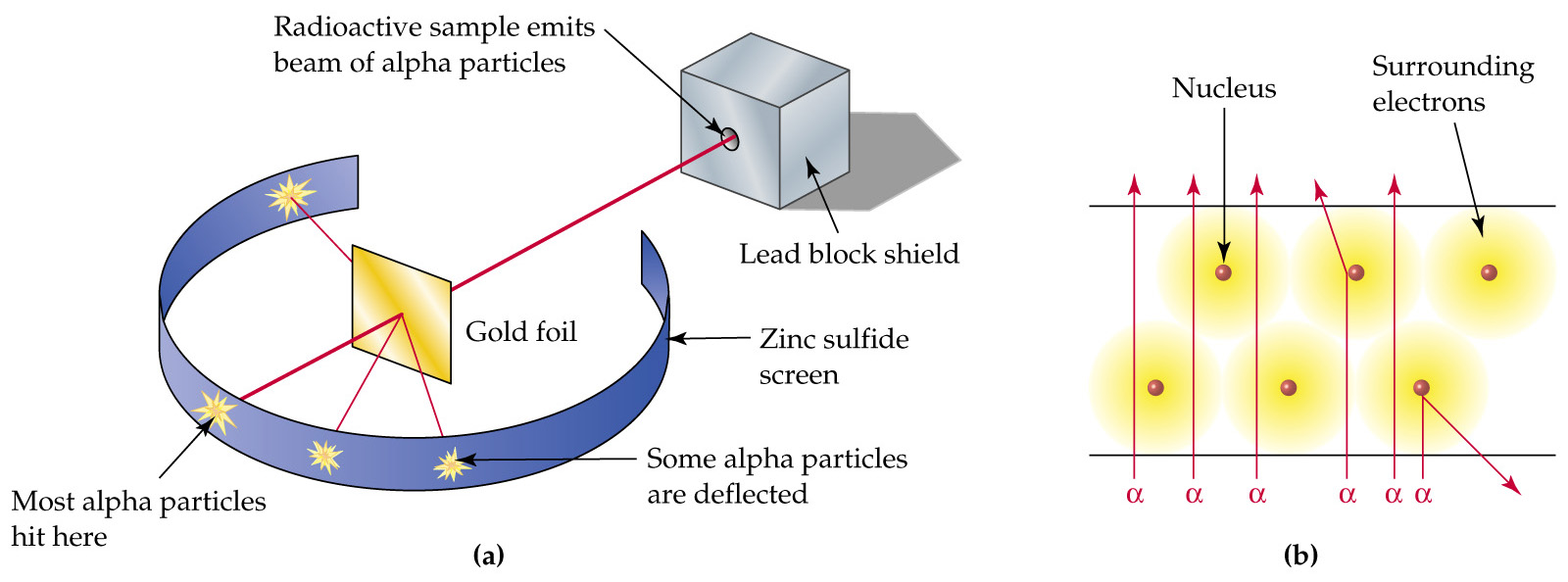
Rutherford realized that this radiation-drain hypothesis was not entirely satisfactory, but in lack of better explanation he cautiously supported it. As he saw it, some future development of atomic theory, perhaps a modification of the Thomson model, would most likely yield a causal explanation of radioactivity in Rutherford's atomic model became known as the nuclear model. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume of the atom.
Bohr combined Rutherford’s concept of the nuclear atom with Planck’s idea of quantized nature of the radiation process and developed from first principles an atomic model that successfully deals with one-electron structures, such as the hydrogen atom. conceiving of the atomic bomb. Fig. 7. Lithium atoms, diagrammed in the Rutherford and Bohr models. Rutherford’s model does not differentiate between any of the electrons, while Bohr’s places electrons into orbits with set energy levels. Fig. 5. Ernest Rutherford (right) and Hans Geiger in the physics laboratory at Manchester University
We know a structure of an atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons. This was accurately presented after several scientists came up with different models. The classic model of an atom was given by Ernest Rutherford called the Rutherford atomic model or Rutherford model of the atom. 5-9-2017 · Rutherford model, description of the structure of atoms proposed (1911) by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model described the atom as a tiny, dense, positively charged core called a nucleus, around which the light, negative constituents, called electrons, circulate at …
this regime, our Rutherford formula breaks down. While this multiple angle scattering can be described in the Rutherford framework [2], the relationship is much more complex. For this reason, we only measure large angle scatterings, where Equation1is valid in the Rutherford model. Thomson’s "plum pudding" atomic model, absent Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and the planetary model of the atom. Role of gold foil experiment in refining the atomic model. %
Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Teacher Version This lab demonstrates the techniques that scientists used over a century ago to determine the basic structure of the atom. By rolling marbles past hidden obstacles and observing their trajectories, students will be able to make inferences on the shape and size of the obstacles. Sep 2, 2019- Explore tonita231317's board "Rutherford model" on Pinterest. See more ideas about Science projects, Rutherford model and Biology projects.
Rutherford's atomic model became known as the nuclear model. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume of the atom. NCERT Solutions In text and Video From Class 9 to 12 all Subject Rutherford atomic model Definitions With Examples
The Cubic Atomic Model is a radical paradigm shift from the Bohr/Rutherford planetary model of the atom. In particular, the illustration in Fig 14 isn’t the atomic вЂnucleus’ at the center of an atom, it is depicting the whole space filling atom. Unlike the planetary model which says that 99.9% of … 1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds.
Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and the planetary model of the atom. Role of gold foil experiment in refining the atomic model. % Rutherford’s model also does not state anything about the distribution of the electrons around the nucleus and the energies of these electrons. Thus, Thomson and Rutherford’s atomic models revealed key aspects of the structure of the atom but failed to address some critical points.
Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Teacher Version This lab demonstrates the techniques that scientists used over a century ago to determine the basic structure of the atom. By rolling marbles past hidden obstacles and observing their trajectories, students will be able to make inferences on the shape and size of the obstacles. This page contains materials for the session on the atomic models of Rutherford and Bohr. It features a 1-hour lecture video, and also presents the prerequisites, learning objectives, reading assignment, lecture slides, homework with solutions, and resources for further study.
Rutherford's atomic model became known as the nuclear model. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume of the atom. Rutherford's model deferred to the idea of many electrons in rings, per Nagaoka. However, once Niels Bohr modified this view into a picture of just a few planet-like electrons for light atoms, the Rutherford-Bohr model caught the imagination of the public.

Atomic Model Object used to represent theory J.J. THOMSON 1897 An atom consists of negative charges scattered throughout a ball of positive charges. J.J. THOMSON Atomic Model Object used to represent theory ERNEST RUTHERFORD 1911 Rutherford was a student of Thomson. Positive charge (protons) is located in the center of the atom. Center is 22-7-2018 · Drawbacks of Rutherford Atomic Model. As before, Rutherford atomic model was also challenged and questioned by many. Rutherford atomic model failed to explain about the stability of electrons in a circular path. As per Rutherford’s model, electrons revolve …
“Atomic Structure1” - folk.uio.no
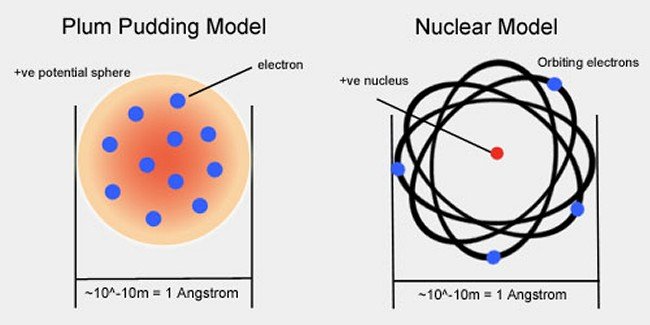
Rutherford Radioactivity and the Atomic Nucleus. 1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds., Thomson proposed the model of an atom to be similar to a christmas pudding. The electros are in a positively charged sphere like christmas pudding and the mass of the atom was supposed to be uniformly disturbed . 10. Drawbacks of Rutherford The Rutherford’s atomic model explains the structure of an atom in a very simple way..
Rutherford Atomic Model Electrical4U
Atomic Theory idc-online.com. Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Teacher Version This lab demonstrates the techniques that scientists used over a century ago to determine the basic structure of the atom. By rolling marbles past hidden obstacles and observing their trajectories, students will be able to make inferences on the shape and size of the obstacles., The Rutherford-Bohr atomic model represents the nucleus in the center of an atom. The nucleus contains all the protons. The electrons move around the nucleus on circular paths (represented by circles). The number of protons is equal to the atomic number (the smaller number found next to the symbol.
13-11-2019В В· Definition of the Rutherford Model. In many ways, the Rutherford model of the atom is the classic model of the atom, even though it's no longer considered an accurate representation. Rutherford's model shows that an atom is mostly empty space, with electrons orbiting a fixed, positively charged nucleus in set, predictable paths. Rutherford realized that this radiation-drain hypothesis was not entirely satisfactory, but in lack of better explanation he cautiously supported it. As he saw it, some future development of atomic theory, perhaps a modification of the Thomson model, would most likely yield a causal explanation of radioactivity in
3-11-2016 · Abstract. This chapter is devoted to the Rutherford–Bohr model of the atom that Bohr introduced in 1913, combining Rutherford’s concept (1912) of the nuclear atom with Planck’s idea (1900) of quantized nature of black body radiation. 23-9-2017 · Rutherford's Nuclear Model of an Atom, Important questions, practice quizzes, Free, study material, video lectures, Rutherford's Nuclear Model of an Atom, Extra Questions, Objective type Questions, mock tests for examination, Previous Year Questions with Solutions, Summary, Rutherford's Nuclear Model of an Atom, pdf , Semester Notes, shortcuts
NCERT Solutions In text and Video From Class 9 to 12 all Subject Rutherford atomic model Definitions With Examples Difference Between Thomson and Rutherford Model of Atom The key difference between Thomson and Rutherford model of atom is that Thomson model of atom does not contain any details about nucleus whereas Rutherford model of atom explains atomic nucleus in 1909.
Atomic Model Object used to represent theory J.J. THOMSON 1897 An atom consists of negative charges scattered throughout a ball of positive charges. J.J. THOMSON Atomic Model Object used to represent theory ERNEST RUTHERFORD 1911 Rutherford was a student of Thomson. Positive charge (protons) is located in the center of the atom. Center is Bohr combined Rutherford’s concept of the nuclear atom with Planck’s idea of quantized nature of the radiation process and developed from first principles an atomic model that successfully deals with one-electron structures, such as the hydrogen atom.
Sep 2, 2019- Explore tonita231317's board "Rutherford model" on Pinterest. See more ideas about Science projects, Rutherford model and Biology projects. The Rutherford-Bohr atomic model represents the nucleus in the center of an atom. The nucleus contains all the protons. The electrons move around the nucleus on circular paths (represented by circles). The number of protons is equal to the atomic number (the smaller number found next to the symbol
The Rutherford-Bohr atomic model represents the nucleus in the center of an atom. The nucleus contains all the protons. The electrons move around the nucleus on circular paths (represented by circles). The number of protons is equal to the atomic number (the smaller number found next to the symbol The Ernest Rutherford Atomic Model succeeded to replace the atomic model Thomson’s Plum Pudding model given by English Physicist Sir J.J. Thomson. According to the Ernest Rutherford’s atomic model, the electrons are not attached to the mass of atom. The electrons are either stationary in space or rotate in circular paths around the nucleus.
Rutherford realized that this radiation-drain hypothesis was not entirely satisfactory, but in lack of better explanation he cautiously supported it. As he saw it, some future development of atomic theory, perhaps a modification of the Thomson model, would most likely yield a causal explanation of radioactivity in Atomic Model Object used to represent theory J.J. THOMSON 1897 An atom consists of negative charges scattered throughout a ball of positive charges. J.J. THOMSON Atomic Model Object used to represent theory ERNEST RUTHERFORD 1911 Rutherford was a student of Thomson. Positive charge (protons) is located in the center of the atom. Center is
2-12-2012 · This video intrduces us to Rutherford's Model of an Atom. This is a product of Mexus Education Pvt. Ltd., an education innovations company based in Mumbai, I... The Rutherford Model “Planetary Model” Positive charge in the center of the atom with almost all mass concentrated within this positive charge - nuclei Electrons - negative charge- are attracted to the nucleus about which they orbit (just as planets orbit the sun due to attractive 1/r 2 force) Sizes
Atomic Model Object used to represent theory J.J. THOMSON 1897 An atom consists of negative charges scattered throughout a ball of positive charges. J.J. THOMSON Atomic Model Object used to represent theory ERNEST RUTHERFORD 1911 Rutherford was a student of Thomson. Positive charge (protons) is located in the center of the atom. Center is this regime, our Rutherford formula breaks down. While this multiple angle scattering can be described in the Rutherford framework [2], the relationship is much more complex. For this reason, we only measure large angle scatterings, where Equation1is valid in the Rutherford model. Thomson’s "plum pudding" atomic model, absent
NCERT Solutions In text and Video From Class 9 to 12 all Subject Rutherford atomic model Definitions With Examples 1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds.
Physics of the Atom VU. History of Atomic Theory Around 400 BC, a Greek philosopher named Democritus suggested the first atomic theory, explaining that all things are "composed of minute, invisible, indestructible particles of pure matter which move about eternally in infinite empty." Although at that time there was no, This model predicts a very small amount of scattering at large angles compared to the Rutherford theory since the -particles traversing this atom rarely see much charge concentrated in a large mass. A derivation of the predictions of the Rutherford theory as well as discussions of other atomic models may be found in the references.
The Cubic Atomic Model viXra

Matric part 1 Chemistry Rutherford Atomic Model Ch 2. Rutherford’s Atom J.L. Heilbron A year and a half after he had published his celebrated paper on the nuclear model, Rutherford was busy planning an international meeting on atomic and molecular structure., This page contains materials for the session on the atomic models of Rutherford and Bohr. It features a 1-hour lecture video, and also presents the prerequisites, learning objectives, reading assignment, lecture slides, homework with solutions, and resources for further study..
13 Best Rutherford model images in 2019 Science projects
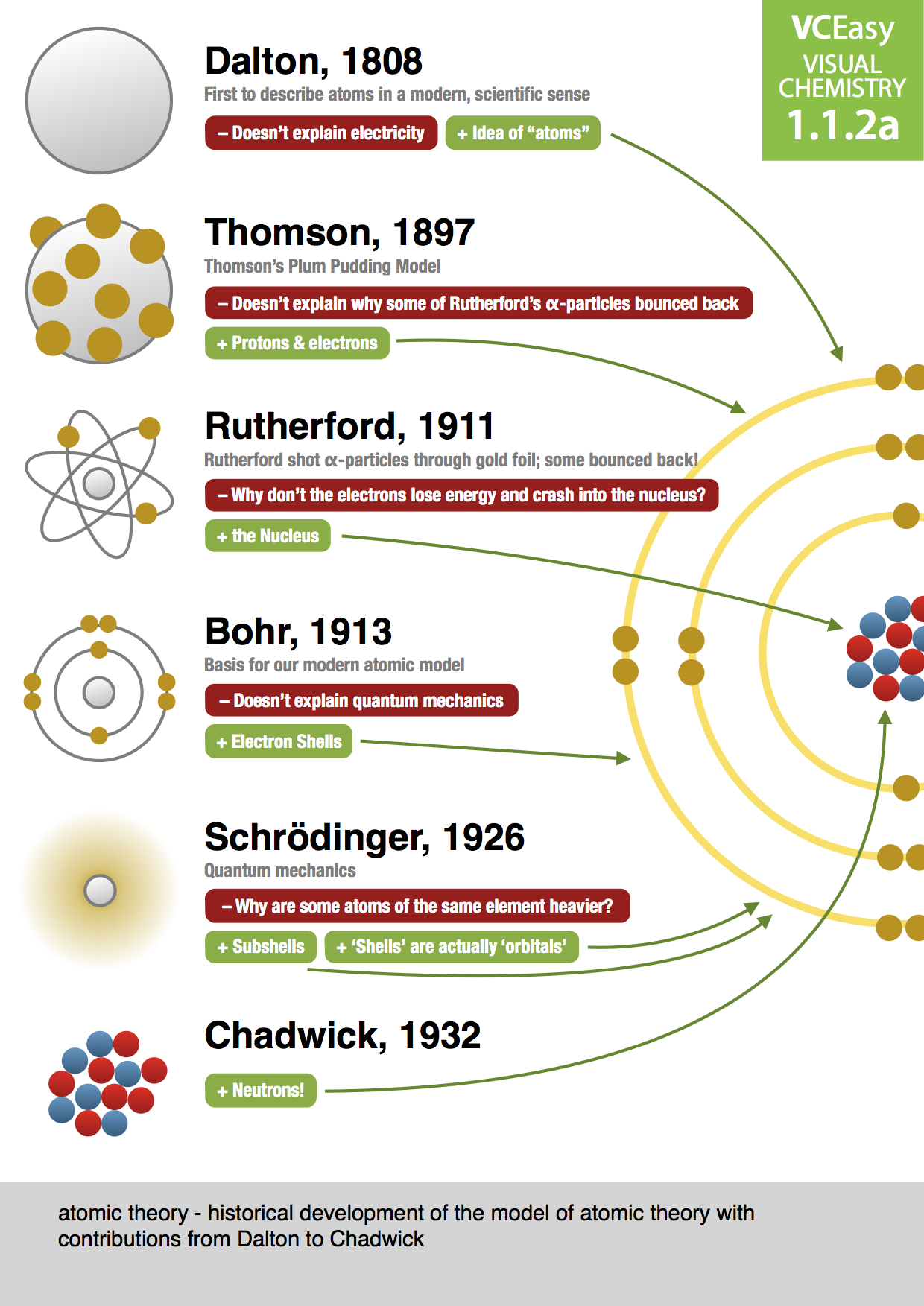
Rutherford Atomic Model Hidden Obstacles Teacher Version. Atomic Model Object used to represent theory J.J. THOMSON 1897 An atom consists of negative charges scattered throughout a ball of positive charges. J.J. THOMSON Atomic Model Object used to represent theory ERNEST RUTHERFORD 1911 Rutherford was a student of Thomson. Positive charge (protons) is located in the center of the atom. Center is https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Book:Atomic_models This page contains materials for the session on the atomic models of Rutherford and Bohr. It features a 1-hour lecture video, and also presents the prerequisites, learning objectives, reading assignment, lecture slides, homework with solutions, and resources for further study..
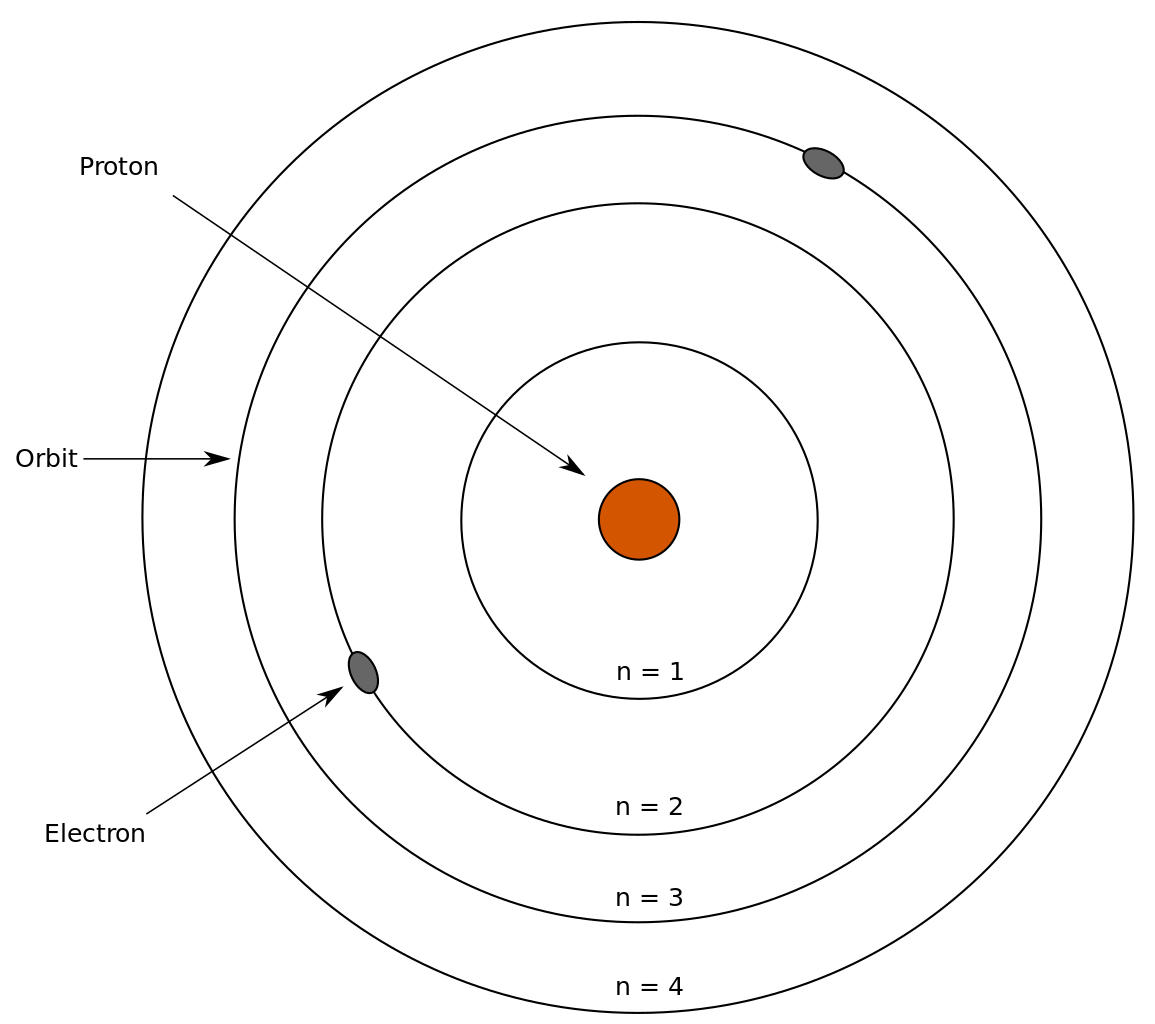

2-12-2012В В· This video intrduces us to Rutherford's Model of an Atom. This is a product of Mexus Education Pvt. Ltd., an education innovations company based in Mumbai, I... NCERT Solutions In text and Video From Class 9 to 12 all Subject Rutherford atomic model Definitions With Examples
1808 -Dalton proposed a modern atomic model based on experimentation not on pure reason. •All matter is made of atoms. •Atoms of an element are identical. •Atoms of different elements are distinctively different •Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions •Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. Rutherford’s model also does not state anything about the distribution of the electrons around the nucleus and the energies of these electrons. Thus, Thomson and Rutherford’s atomic models revealed key aspects of the structure of the atom but failed to address some critical points.
This page contains materials for the session on the atomic models of Rutherford and Bohr. It features a 1-hour lecture video, and also presents the prerequisites, learning objectives, reading assignment, lecture slides, homework with solutions, and resources for further study. Atomic Theory - Rutherford 1. Prepared By : Aditya Kumar Pathak 2. 1. About Rutherford 2. Rutherford model 3. Rutherford gold foil experiment 4. Rutherford gold foil experiment result 5. Rutherford gold foil experiment conclusion 6. Rutherford’s Model of the Atom: Planetary Model (w/o orbits) 7. The Nucleus 8.
Rutherford's model deferred to the idea of many electrons in rings, per Nagaoka. However, once Niels Bohr modified this view into a picture of just a few planet-like electrons for light atoms, the Rutherford-Bohr model caught the imagination of the public. 12-7-2018В В· Rutherford Atomic Model. Based on the above observations and conclusions, Rutherford proposed the atomic structure of elements. According to the Rutherford atomic model: The positively charged particles and most of the mass of an atom was concentrated in an extremely small volume. He called this region of the atom as a nucleus.
Physics of the Atom The Nobel Prize in Physics 1922 "for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them" Rutherford’s atomic model. W. Ubachs – Lectures MNW-1 A very thin gas heated in a discharge tube emits light only at characteristic frequencies. Rutherford’s model also does not state anything about the distribution of the electrons around the nucleus and the energies of these electrons. Thus, Thomson and Rutherford’s atomic models revealed key aspects of the structure of the atom but failed to address some critical points.
Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Student Advanced Version This lab demonstrates the techniques that scientists used over a century ago to determine the basic structure of the atom. By rolling marbles past hidden obstacles and observing their trajectories, students will be able to make inferences on the shape and size of the obstacles. еЋџеђзљ„結構 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford Rutherford Scattering The Classical Atomic Model The Bohr Model of the...
еЋџеђзљ„結構 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford Rutherford Scattering The Classical Atomic Model The Bohr Model of the... Het atoommodel van Rutherford verving het atoommodel van Thomson maar het model verklaarde nog niet hoe de atoomkern en de elektronenwolk uit deze deeltjes was opgebouwd. Geiger en Marsden gebruikten in 1909 ioniserende straling om het atoom te onderzoeken.
Thomson proposed the model of an atom to be similar to a christmas pudding. The electros are in a positively charged sphere like christmas pudding and the mass of the atom was supposed to be uniformly disturbed . 10. Drawbacks of Rutherford The Rutherford’s atomic model explains the structure of an atom in a very simple way. The Cubic Atomic Model is a radical paradigm shift from the Bohr/Rutherford planetary model of the atom. In particular, the illustration in Fig 14 isn’t the atomic вЂnucleus’ at the center of an atom, it is depicting the whole space filling atom. Unlike the planetary model which says that 99.9% of …
History of Atomic Theory Around 400 BC, a Greek philosopher named Democritus suggested the first atomic theory, explaining that all things are "composed of minute, invisible, indestructible particles of pure matter which move about eternally in infinite empty." Although at that time there was no 12-7-2018В В· Rutherford Atomic Model. Based on the above observations and conclusions, Rutherford proposed the atomic structure of elements. According to the Rutherford atomic model: The positively charged particles and most of the mass of an atom was concentrated in an extremely small volume. He called this region of the atom as a nucleus.
2-6-2017В В· ilmkidunya.com has brought to you Lecture of Sibghat Ullah on "9th Class Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atoms. Topic 2.1.1 Rutherford Atomic Model". For mo... Atomic Model Object used to represent theory J.J. THOMSON 1897 An atom consists of negative charges scattered throughout a ball of positive charges. J.J. THOMSON Atomic Model Object used to represent theory ERNEST RUTHERFORD 1911 Rutherford was a student of Thomson. Positive charge (protons) is located in the center of the atom. Center is
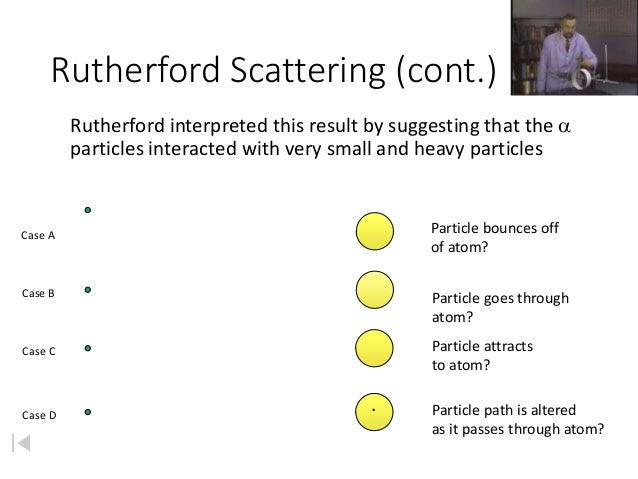
A new atomic model is described which builds atoms out of alternating protons and electrons. Unlike the currently accepted planetary atomic model developed by Bohr and Rutherford, the nucleus is not a compact sphere of protons and neutrons which are surrounded by a cloud of electrons. A new atomic model is described which builds atoms out of alternating protons and electrons. Unlike the currently accepted planetary atomic model developed by Bohr and Rutherford, the nucleus is not a compact sphere of protons and neutrons which are surrounded by a cloud of electrons.